Some three years ago we began our shift from one ancient Shropshire town and into another: out of Much Wenlock and into Bishop’s Castle. The first was a settlement that grew up outside the walls of Wenlock Priory, its inhabitants subject to rule by Prior until the Dissolution in 1542. The second evolved, or rather descended from a hillside motte and bailey castle, built around the 1080s by the Bishops of Hereford, owners of the surrounding manor lands of Lydbury North.
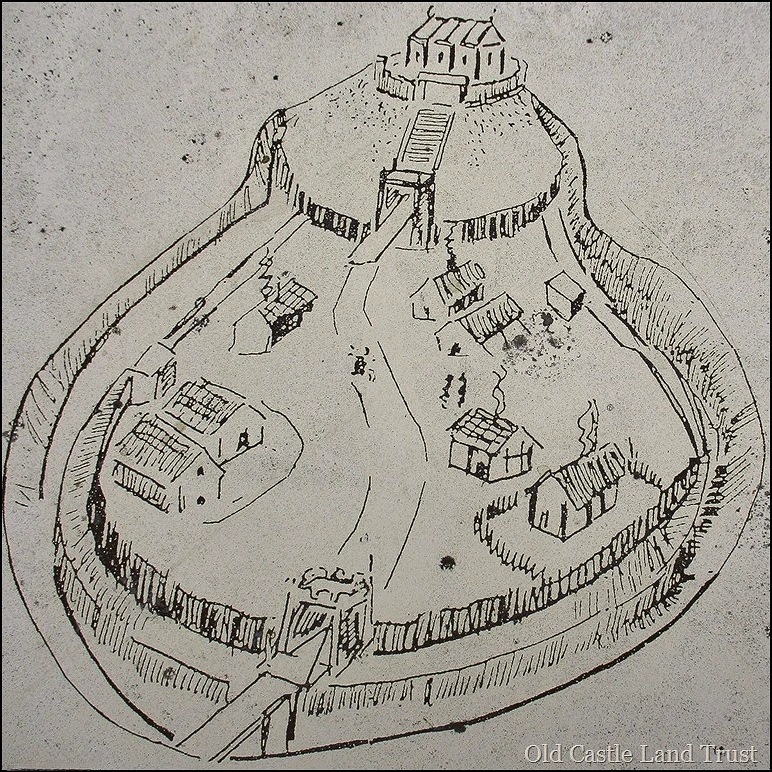
Notional reconstruction of the earth and timber motte and bailey of 1080s CE
*
The castle was deemed essential for the defence of the manor, given its location close to the Welsh border and potential raiding parties. It also served as an administrative centre for running the estate, gathering taxes and holding courts to maintain law and order. The Bishops had pastoral duties too, but for the ordinary souls who lived and worked on their lands, their worldly purpose was to produce good crops and profits for their landlords, who in turn had their own obligations to the Crown. It was big business then; a feudal corporation.

*
It is not clear how the bishops of a town nearly 40 miles away came to own Lydbury North, a highly profitable farming domain. But, as often happened in medieval times, there was a handy legend to lend authority to claims of possession. (In Much Wenlock it was the apparent 11th century discovery of St. Milburga’s shining seventh century bones that helped turn the town into a busy pilgrim centre).
In similar vein, the Bishop’s Castle legend has it that around the 790s CE, the original Lydbury North owner, Saxon lord, Egwin Shakehead, was so grateful to have his tremors cured at St. Ethelbert’s tomb in Hereford Cathedral, he gave the 18,000 acre estate to the bishops in perpetuity. It is a compelling blend of antique ‘authority’ and saintly miracle, probably politically expedient in the immediate post-Conquest era of the Norman regime change.
The Bishops’ motte and bailey was thus built in line with the prevailing Norman subjugation plan to establish fortifications across England and Wales. The earth and timber mottes were fairly quick to construct. Later they would be rebuilt in stone, depending on strategic need. But in any event, they were highly visible structures to remind the Saxons and Celtic Welsh of who was in charge.
It was also Norman policy to develop civilian settlements next to their castles, this to secure the site and to ensure neighbouring land was cultivated. And so began the ‘planted’ town of Bishop’s Castle with the provision of dwellings for rent. These were established either side the castle’s main access road, running down from the outer bailey walls and towards the church.
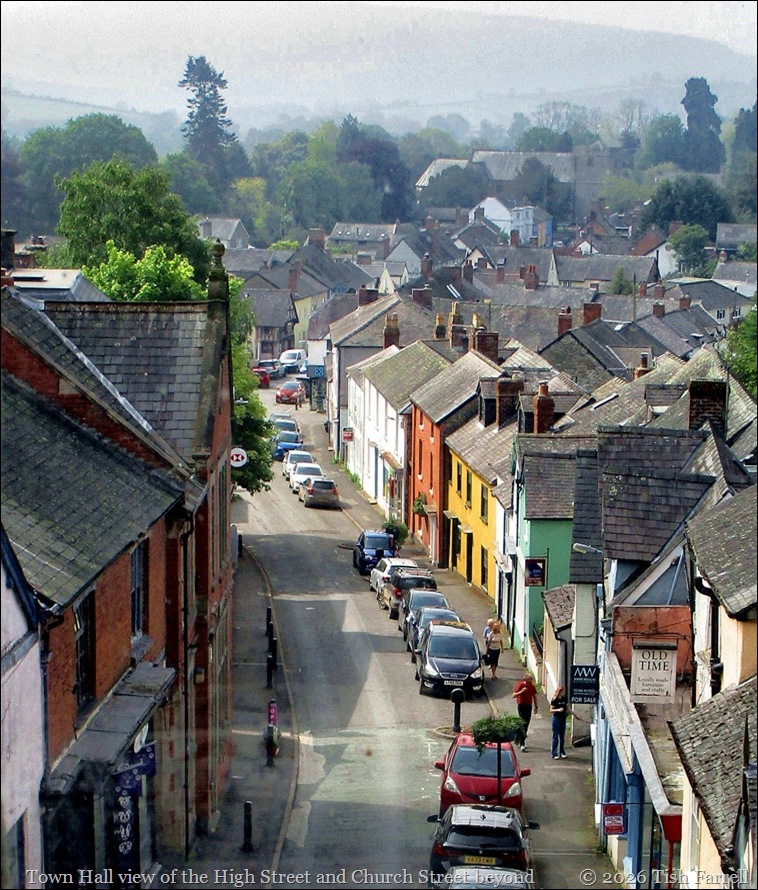

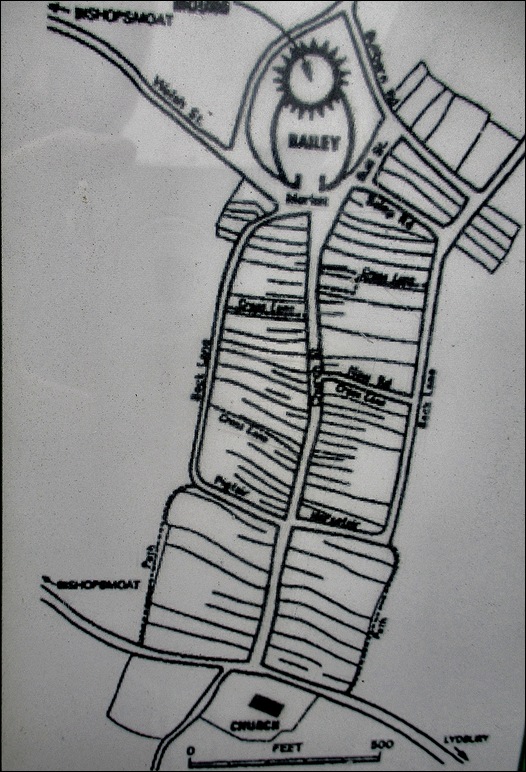
Now you need to look at the High Street with fresh eyes: strip away all those slate roofs and hugger-mugger back-lot buildings. See, not the tall eighteenth and nineteenth century facades, but low, timber-framed, thatched dwellings fronting the road. Behind each cottage would be a long narrow garden or burgage plot for the tenant’s use. At the foot of these, on both sides and running parallel to the main street, were ‘back lanes’. And beyond the lanes, to the east and west, were the town fields.
You can get the gist from this rather blurry photo from one of the town’s information boards.
*
By 1167 there were 47 burgages, and the town was on the up. At that time, too, the castle was rebuilt in stone, and grand enough to host both bishops’ and royal visitations.
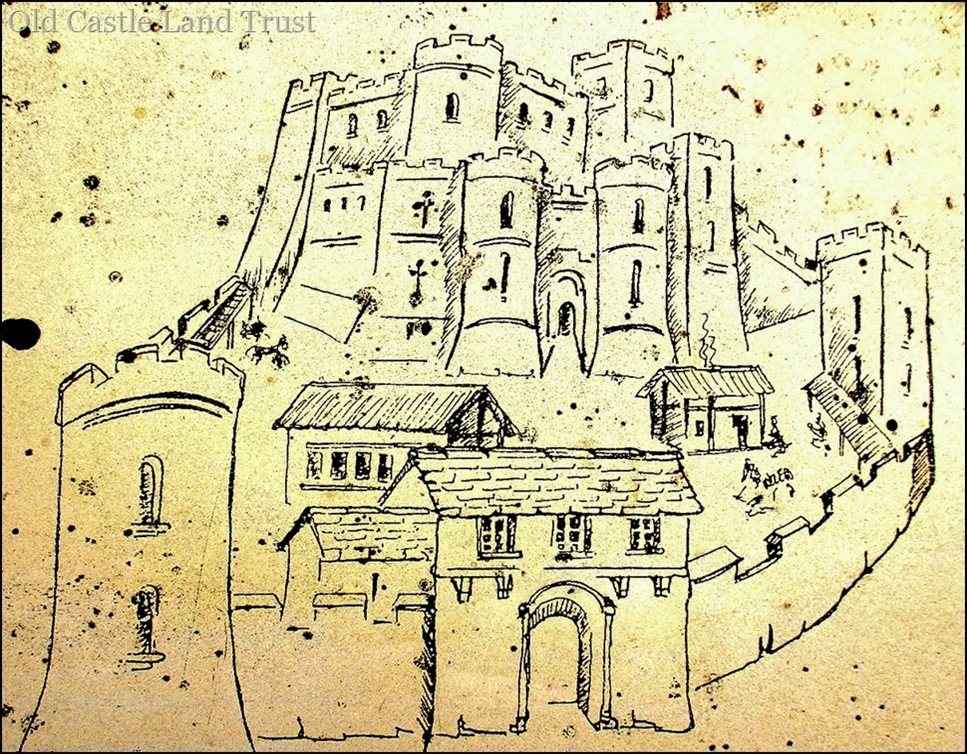
This following reconstruction is again notional, but it suggests there was both an outer bailey with service buildings such as stables, stores, brewery and bakehouse, and a defended inner bailey surrounding the main castle keep.

*
Over the following centuries the ‘new town’ prospered. Weekly markets and annual fairs were well supported, and local trades, servicing both castle and general populace, likewise flourished. The bishops continued to reap the benefit of course, and it wasn’t until 1559 that they lost control. Queen Elizabeth 1 forced the then Bishop Scory to surrender his four richest manors to the Crown in return for less wealthy ones. (The Bishop had been implicated in a domestic financial scandal). The exchange included Bishop’s Castle.
At this time, too, there was a Crown survey of the castle. It recorded the presence of thirteen habitable rooms, the roofs leaded. There was a tower containing stables on the east wall, a prison tower, dovecote and other buildings. The castle had its own garden, forest and park.*
*
There are few signs of the castle today, apart from the Castle Green (cared for by Old Castle Land Trust), a small grassy segment of the original bailey.
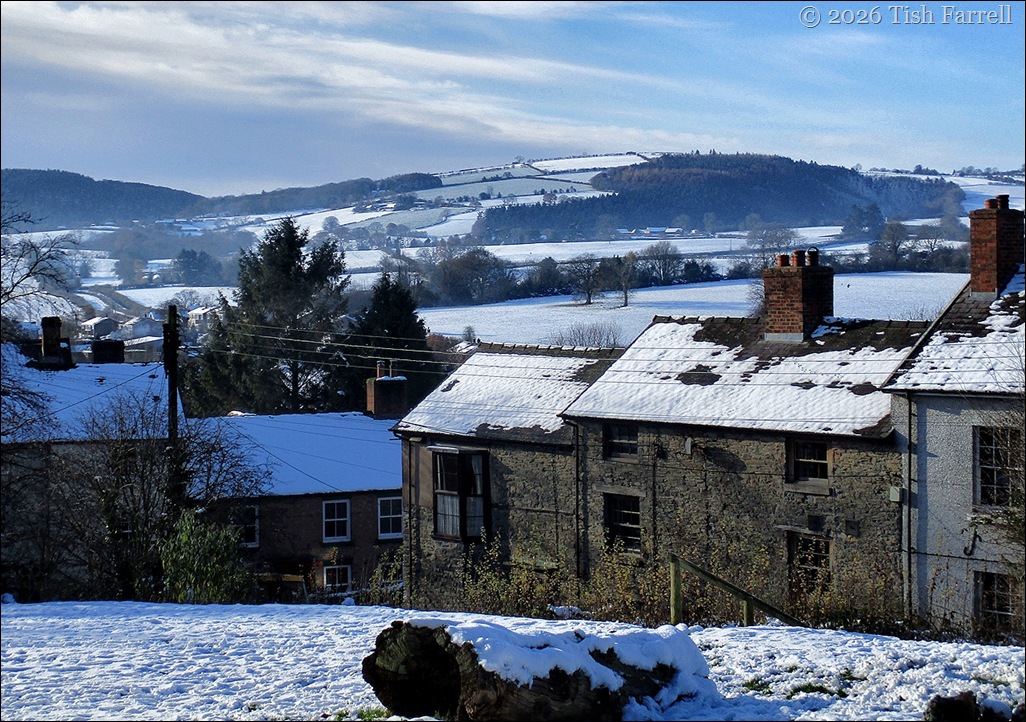

*
The castle played no role in the Civil War of the mid 1600s. In fact by then it was reported derelict, with its roofs stripped of lead, and its stone and timbers used in developing the town’s housing. The recycling of materials probably became a matter of course. One beneficiary was The Castle Hotel, built in 1719 within the outer bailey.
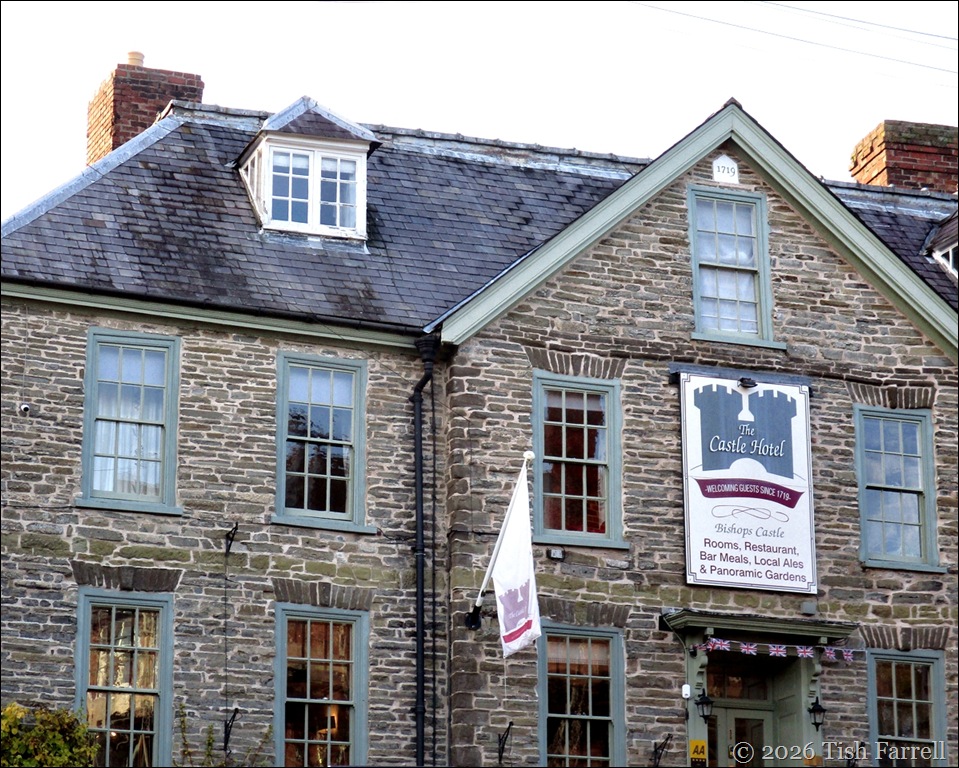

*
Around this time, too, the site of the castle keep, which was further up the steep hill behind the hotel, was levelled to make a fine octagonal bowling green. Both the green and the restored octagonal pavilion are still in use today.
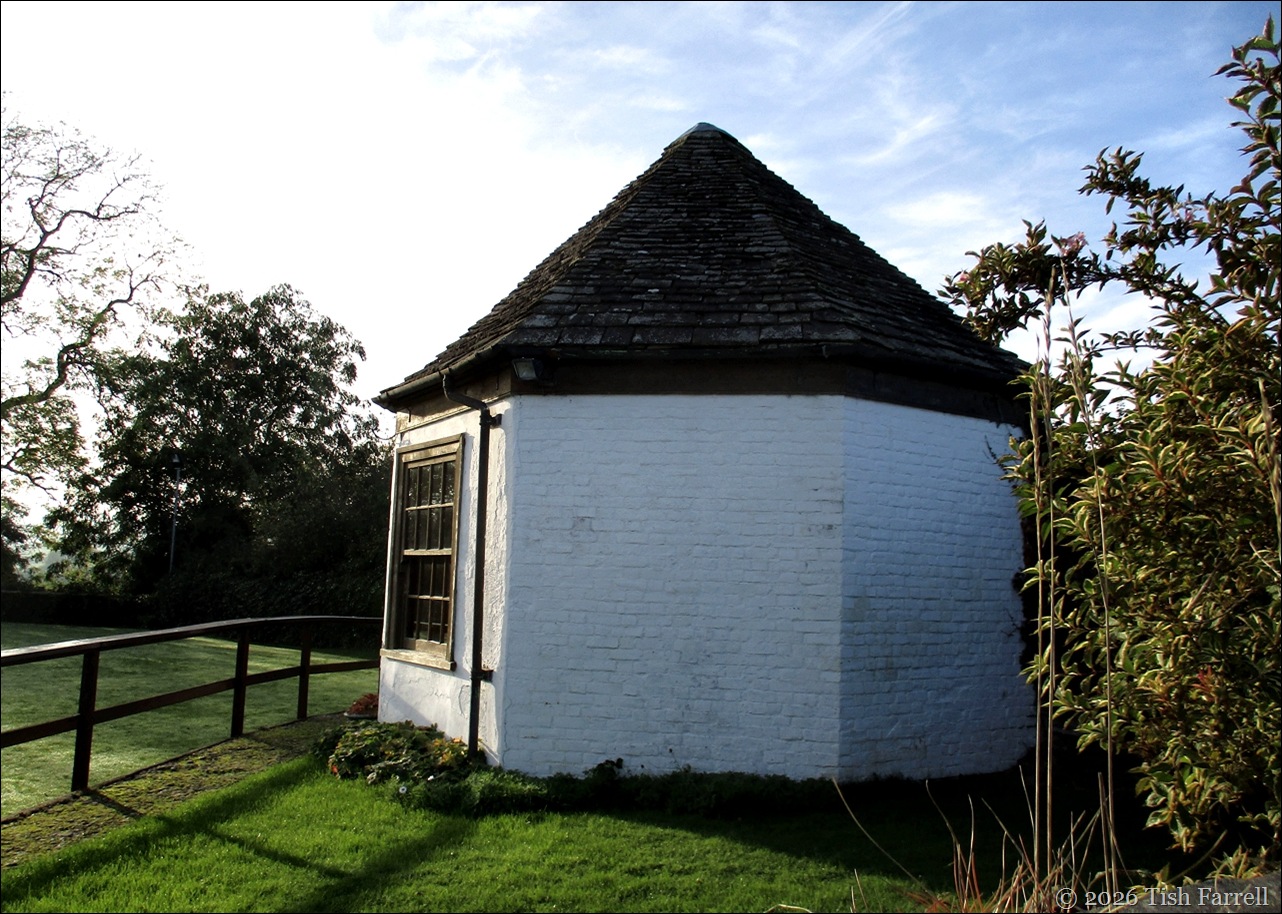

The Bowling Green Pavilion
*
So here we are at the bowling green at the top of the town. But for the best view we need to drop down a level to the garden above The Castle Hotel (its rooftops in the foreground).
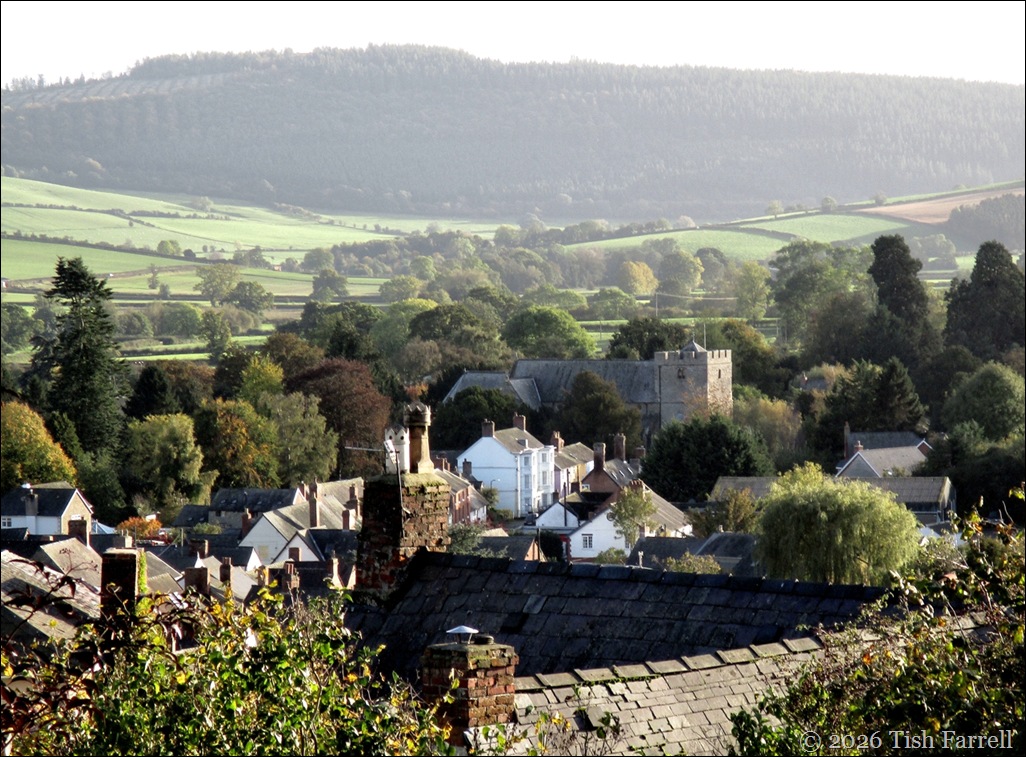

I’m guessing I was standing near or within the site of the inner bailey when I took this photo. And am I sorry there’s no castle rampart left to clamber up and take more dramatic photos? No, not really. Castles can be exciting structures, but I’m thinking our response to them often has more to do with romance than reality.
I’ve anyway learned that the born-and-bred locals call their castle-less town ‘the Castle’, its utterance conveying a strong sense of community and long rootedness, yet with fellow-feeling enough to absorb generations of blow-ins; people like us. And so it seems that although the castle fabric may be long gone, what remains feels a better kind of stronghold.
*
Sources:
*The Story of Bishop’s Castle 2018 eds David Preshous, George Baugh, John Leonard, Gavin Watson, Andrew Wigley; Logaston Press
Bishop’s Castle: A Timeline of Governance Bishop’s Castle Heritage Resource Centre
Copyright 2026 Tish Farrell














































































